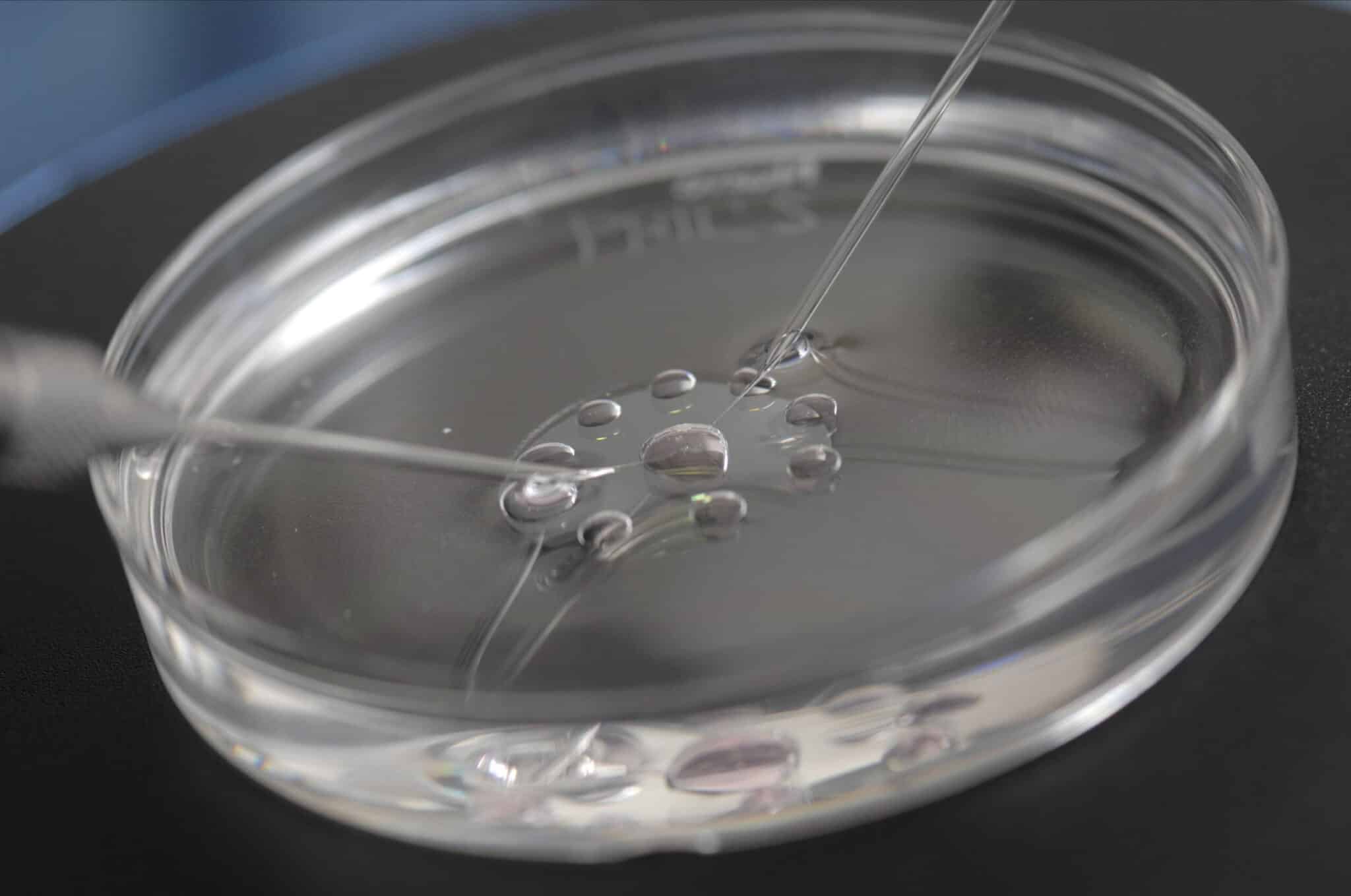
In vitro fertilization or IVF is a type of medical technology that helps women and couples with reproduction. In vitro fertilization is completed by extracting eggs from the woman, getting a sperm sample, and manually bringing the egg and sperm together in a laboratory Petri dish. Afterward, the embryo is moved to the woman's uterus.
The very first case of in vitro fertilization occurred in 1978 in England when Louise Brown was the first baby conceived outside her mother's womb. This form of fertility assistance has been around ever since and began to take off in the 1980s. However, due to the high cost of this treatment, many people worry whether or not it will actually work in their case.
How Likely is it that In Vitro Fertilization will Work?
The rate of success for this form of reproductive technology depends greatly on a variety of different issues such as how old the woman is, the reproductive history of the couple, lifestyle factors, and the cause of the infertility. The success of in vitro fertilization depends significantly on the age of the female.
The normal success rate for women under 35 is around 25% per cycle, this then drops quickly to 10% for women around 40.
Success rates at foreign clinics appear to be higher because, among other things, they screen embryos for chromosomal defects (PGT-A) but also because they increasingly use egg donation.
These are typical success rates of foreign clinics, here as an example the success rates of the IVF Clinic Düna in Northern Cyprus: (https://www.dunyaivf.com/en/ivf-success-rates/)
Age 20-29: 51%
Age 30-34: 47%
Age 35-39: 43%
Age 40+: 14%
However, pregnancy rates are not the same as live birth rates. The miscarriage rate ranges from 10% to as much as 30%, depending on the age of the women, or even higher, depending on whether the embryo was screened for chromosomal defects or not.
The Factors that Impact Successful In Vitro Fertilization
According to the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology, there are many factors, especially age that impact the success rate of pregnancy among clinics. The success rates decline as women get older such as those who are more than 35 years old. There is a higher miscarriage rate among older women especially those who are above 40 years old.
In addition, the number of embryos that are transferred is a factor that impacts pregnancy. Transferring more embryos at one time does not actually impact the chance of a live birth at high rates. However, it does impact the likelihood of multiple fetuses and the relevant risks associated with it.
Patients' characteristics and medical history before in vitro fertilization also impacts the number of embryos that should be transferred and the success rate of pregnancy. Due to all of these factors, it may take multiple cycles of this process before a woman with fertility difficulties may become pregnant.
What are the Reasons for Needing Reproductive Assistance?
In vitro fertilization along with other reproductive technologies is often used to help patients who are infertile due to:
- A genetic disorder
- Endometriosis
- A uterine fibroid
- Ovulation disorders and premature ovarian failure
- Removed fallopian tubes
- Male infertility such as low sperm count or sperm motility
- Sperm issues where these cells are unable to penetrate or survive in the cervical mucus
- Damaged fallopian tubes
- Antibody issues that damage the sperm or eggs
- Another unexplained fertility problem
All of these factors also impact the success rates associated with pregnancy and infertility. What can you expect when you begin in vitro fertilization? Below are a number of steps you'll need to be aware of.
The Five Steps of In Vitro Fertilization
The embryo transfer process includes five basic steps. First, fertility medication is taken to essentially stimulate the woman's egg production. This is meant to stimulate multiple eggs at the same time because some of the eggs may not develop. In addition, a transvaginal ultrasound is taken and blood work is conducted on the woman.
The second step includes retrieving the eggs from the woman through a minor surgery where an ultrasound imaging process is used while inserting a needle through the pelvic cavity to remove eggs. The woman is given pain medicine to remove any discomfort during the surgical procedure.
During the third step, the man is asked to provide a sperm sample that will be combined with the woman's eggs. The fourth step is called insemination. During this process, the sperm and eggs are combined and then stored in a Petri dish to stimulate fertilization.
At times, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is used during this process. This means a sperm cell is directly injected into the egg to reach fertilization. The eggs are then monitored to make sure fertilization and cell division occurs. Afterward, the sample is considered an embryo.
The last step is when the embryos are transferred into the woman's uterus. This usually occurs three to five days after the eggs were retrieved from the woman. Either a small tube or catheter is used to transfer the embryos. Usually, this is relatively painless but some women do experience cramping.
The woman usually stays in a hospital bed for several hours afterward. She is discharged four to six hours after the procedure. If everything is successful, often the embryo is implanted six to 10 days after the egg was first retrieved. Two weeks after the embryo transfer, the doctor likely performs a pregnancy test.

«The miscarriage rate is rarely listed: it ranges from 10% to 30% or even higher, depending on the age of the woman and whether the embryo was screened.»
Risks and Side Effects of In Vitro Fertilization
It is also important to consider the risks and side effects that a woman may undergo when choosing this form of fertility treatment. She may experience bruising and soreness at the drug injection site, nausea and vomiting, mood swings, fatigue, allergic reactions such as itchy or red skin, breast tenderness, vaginal discharge, and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome can lead to dehydration, trouble breathing, and abdominal pain. In very rare cases, this can also lead to blood clots and liver failure. The egg retrieval process can lead to pelvic and abdominal pain, potential injuries to organs near the ovaries, and pelvic infection. Women who undergo embryo transfer tend to experience mild cramping and slight vaginal bleeding. In rare cases, an infection may occur.
Other Issues to Consider with Fertility Treatment
It is important to note that any embryos that a couple or woman doesn't use in the first attempt toward pregnancy can be frozen for later implantation in case the first attempt is not successful. This can save money if a woman does go onto a second or third cycle of in vitro fertilization.
However, if a couple does not want the leftover embryos, they can donate them to another infertile couple or ask the clinic to destroy the samples. Both the man and woman must agree before the embryos can be donated or destroyed.
Based on the low success of in vitro fertilization among older patients and the potential risks involved in this form of fertility treatment, couples and single women will need to consider all of their options and decide for themselves the best way to start their family and where to get fertility treatment.
